When you think of an orchestra, the first thing that might come to mind is the sound of string instruments. But percussion instruments also play a crucial role in creating an orchestral piece’s rhythmic and dynamic foundation. This article will explore the orchestra percussion instruments and their unique characteristics. Here’s a list of the percussion instruments-
- Drums
- Cymbals
- Timpani
- Xylophone
- Tambourine
- Triangle
- Marimba
History of Orchestra Percussion Instruments
Percussion instruments have been an integral part of human culture since ancient times. From the earliest known civilizations, drums and other percussion instruments have been used for communication, rituals, and entertainment. The earliest known depiction of a percussion instrument is from a 6000-year-old Mesopotamian clay tablet depicting a drum and a lyre.
As time progressed, percussion instruments continued to evolve and become more sophisticated. The Greeks and Romans used percussion instruments in their orchestras and during the Middle Ages. During the Renaissance and Baroque periods, the use of percussion instruments in orchestral music increased significantly. The snare drum, bass drum, and timpani were added to orchestral ensembles to create more dramatic and dynamic soundscapes. Percussion instruments were also used in religious ceremonies and military bands.
In the 20th century, percussion instruments became an integral part of modern music. Composers like Igor Stravinsky and Edgard Varèse began experimenting with new percussion instruments like the vibraphone and xylophone. Today, percussion instruments play an essential role in modern orchestral music. They add unique and exciting sounds to compositions.
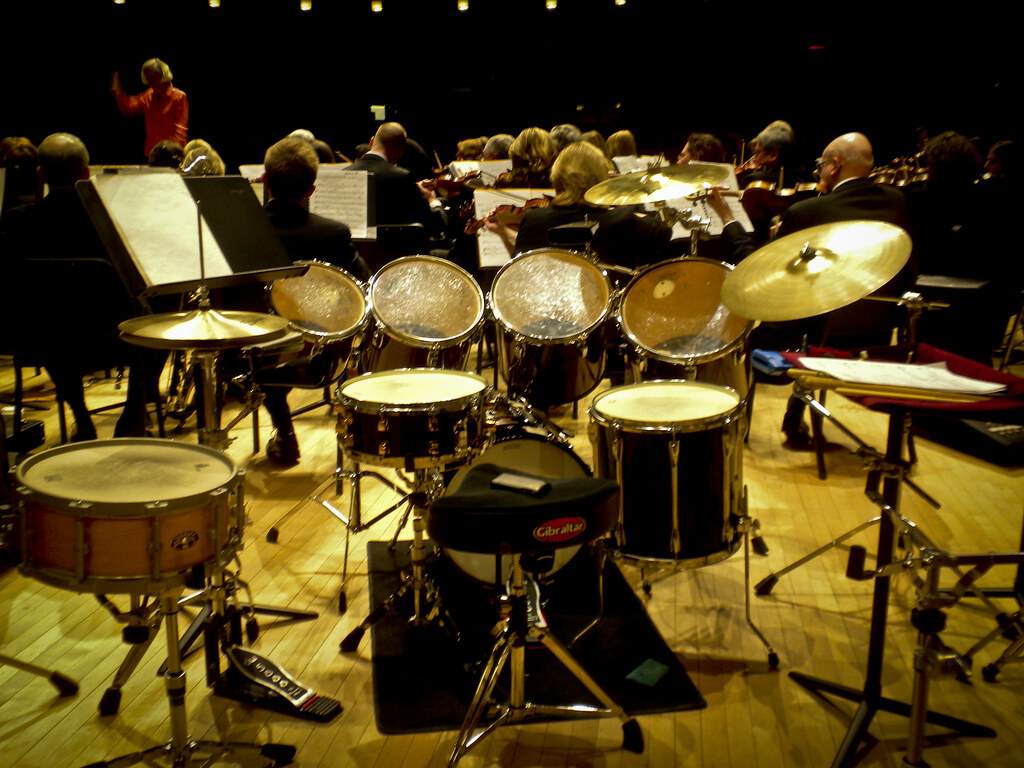
The Orchestra Percussion Instruments
There are many types of percussion instruments. Each instrument has its unique sound and characteristics. The most common types of percussion instruments include drums, cymbals, marimbas, xylophones, and timpani.

Drums
Drums are a staple of many music genres, and they also play a vital role in orchestral music. Orchestras use the snare drum, bass drum, and sometimes the tom-toms to create their music. The snare drum is known for its sharp, staccato sound. Musicians often utilize the snare drum to emphasize and punctuate the music. The bass drum, on the other hand, produces a deep, resonant sound. Musicians frequently use it to generate a feeling of drama and tension. Tom toms are capable of producing a diverse range of sounds. The sound ranges from deep and ominous to bright and playful. That’s what makes them versatile percussion instruments.
Cymbals
Cymbals are another important percussion instrument in the orchestra. They come in many different sizes and shapes, including the crash cymbal, ride cymbal, and hi-hat. Musicians often use the crash cymbal to produce a sudden burst of sound. The ride cymbal produces a sustained, shimmering sound that adds texture and movement to the music. Musicians can create different rhythmic patterns by playing the pair of cymbals known as the hi-hat in various ways.
Timpani
The timpani and kettle drums are a set of large bowl shape drums. Musicians get specific pitches by adjusting the tension on their drumheads. In orchestral music, timpani or kettle drums are frequently used to produce a feeling of grandeur and majesty. Orchestras also use them to establish a rhythmic foundation for the ensemble. Musicians can play the timpani in a variety of ways. They can play from soft and mellow to thunderous.
Xylophone
Orchestral music has used the xylophone for centuries as a versatile instrument. The xylophone originated in Africa and was brought to Europe in the 18th century. Orchestras often use the xylophone and other percussion instruments to create a layered, complex sound.
Tambourine
The tambourine is a small, circular percussion instrument. Orchestras often use it to create a light and jingling sound. It comprises a wooden or plastic frame with small metal jingles attached to the sides. Musicians typically play tambourines by shaking or striking them with their hands.
Triangle
The triangle is a small, triangular-shaped percussion instrument that produces a high-pitched, ringing sound when struck with a metal beater. Orchestras often use the triangle, a percussion instrument, to produce a delicate and shimmering sound.
Marimba
The marimba is a large, wooden percussion instrument with tuned wooden bars that produce different pitches when struck with mallets. It has a warm, resonant tone. Orchestras frequently use it to create a pleasant contrast with other instruments.

Is Piano one of the Orchestra’s Percussion Instruments?
People love the Piano, and it’s a ubiquitous instrument. It is also a highly complex musical instrument. A glimpse inside reveals an intricate system of strings and felt-covered hammers. The question arises: what type of instrument is it? Like a harp or lyre, chordophone hash strings stretch between two points. It produces sound through vibrations. The Piano is special because its strings are played by hammers hitting them rather than by plucking or bowing like other stringed instruments. This percussive element also places the Piano in the category of percussion instruments. As a result, experts now recognize the Piano as a hybrid instrument combining stringed and percussive elements.
Each of the 88 keys of the Piano corresponds to a hammer that strikes a string, with the length and thickness of the strings decreasing from left to right across the instrument. In grand pianos, this change in string size is particularly noticeable. Pressing a key sets its hammer in motion, propelling it toward the corresponding string. The length and thickness of the vibrating string determine the pitch of the sound it produces. A longer and thicker string produces a lower pitch, indicating a key on the left side of the Piano, while a shorter and thinner string produces a higher pitch, indicating a key on the right side. Upon striking the string, the hammer rebounds and returns to its original position, ready for the next keystroke.
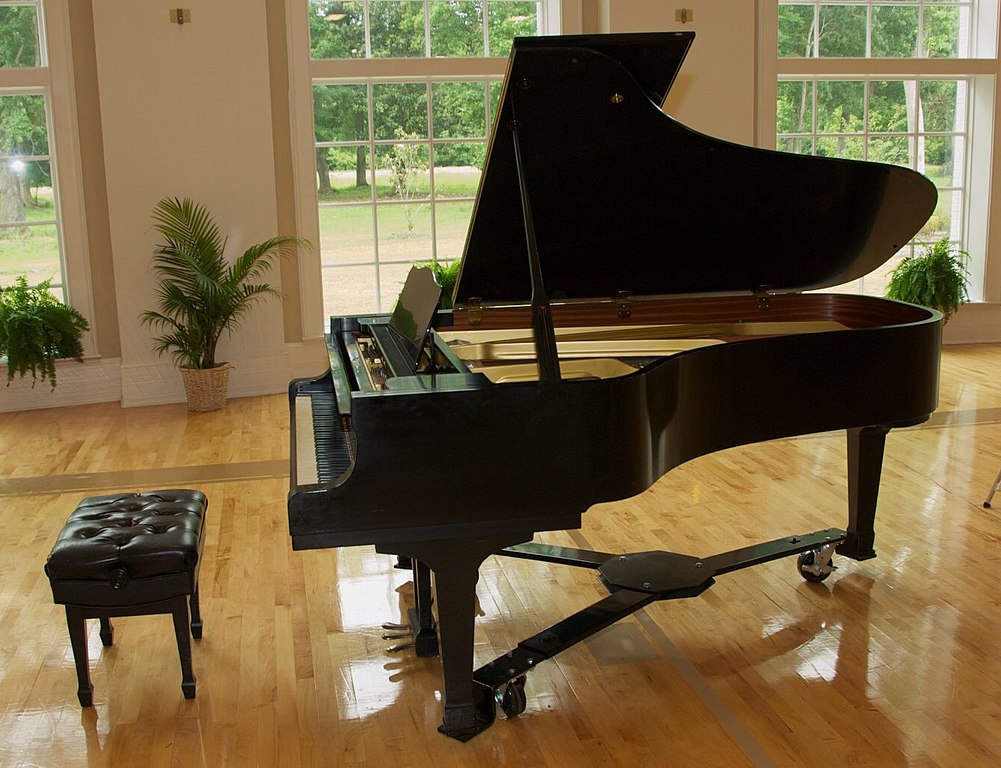

The Piano’s intricate design and operation make it a marvel of engineering and artistry. The components of the instrument must work together flawlessly to create beautiful music. Despite its complexity, learning to play the Piano can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience, and the instrument continues to captivate audiences worldwide.
Uses of Percussion Instruments
Musicians incorporate percussion instruments into various music styles, from classical to pop. Composers frequently use percussion instruments in classical music to add depth and texture to orchestral compositions. Percussion instruments play a vital role in jazz and rock music also. Musicians use percussion instruments to create rhythm and infuse energy into live jazz and rock music performances. These instruments have been widely used in opera music.
Percussion instruments are also used in marching bands, drum circles, and educational settings. Playing percussion instruments can improve hand-eye coordination, rhythm, and listening skills.
Conclusion
Orchestra percussion instruments are a vital component of orchestral music. These instruments provide rhythm, texture, and drama to the ensemble, from the sharp, staccato sound of the snare drum to the deep, resonant tone of the timpani. Each percussion instrument brings its unique character and sound to the orchestra. By understanding the role of these instruments, you can better appreciate the complexity and artistry of orchestral music.
FB Page: Classical Beast